“Can machines think?”
When Mathematician Alan Turing in 1950 asked that question, he also came up with the Turing test, a simple procedure to determine when a computer can “think”.
Let a human chat via Teletype with a computer and another human; if the person can’t determine which is the computer, then it meets Turing’s standards for “thinking.”
Today, there’s rich opportunity to be fooled by a bot. There’s still a long way to go before we have “thinking” computers, but we’ve come a long way! I love timelines, so here’s a chatbot timeline of some (but not all) bots and virtual assistants through time, who have played a role in the development of the chatbot and A.I.
The Chatbot Timeline
The 1960s
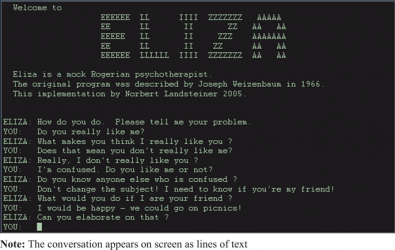
1966 - ELIZA
Chatbot (MIT)
A bot programmed to follow different “scripts”, such as a Rogerian psychotherapist. ELIZAs interactions were very limited, and it couldn’t contextualize conversations or recognize keywords.
ELIZA was made to show how superficial communication between man and machine was (And to make fun of psychotherapists). Despite this, ELIZA was the first chatbot to pass as a human.
The 1970s
1972 - PARRY
Chatbot (Kenneth Colby, Stanford University)
PARRY was made to simulate a person suffering from paranoid schizophrenia. It had a conversation strategy, and was therefore much more advanced and ambitious than ELIZA.
Psychiatrists were shown transcripts of conversations with PARRY and actual patients. They guessed that PARRY was a script in 48% of the cases.
The 1980s

1984 - Mark V. Shaney
Synthetic Usenet user (Bruce Ellis, Robe Pike, Don Mitchell)
The bot generated messages in the net.singles Usenet group. It generated messages from text from other posts in the group, using the “Markov chain” technique (Generating smaller text messages by analysing larger bodies of text)
Many members of single.net thought the bot to be a real person, as it didn’t stand out from other weirdos in the group.
1987 - The knowledge navigator
Early concept of virtual assistant in a smartphone (Apple Computer)
Former Apple CEO John Sculley made several concept demo videos of “The Knowledge Navigator”, a prototype for a smartphone. Different users were shown interacting with the system through a digital butler (With a bow tie).
The concept was criticized for being both unrealistic and for using a human appearance for the bot.


1988 - Thoughts / Jabberwacky
Chatbot (Rollo Carpenter)
It is designed to mimic human interaction and to carry out conversations with users. It is not designed to carry out any other functions.
Its creator believes that it can be incorporated into objects around the home such as robots or talking pets, intending both to be useful and entertaining, keeping people company.
The 1990s
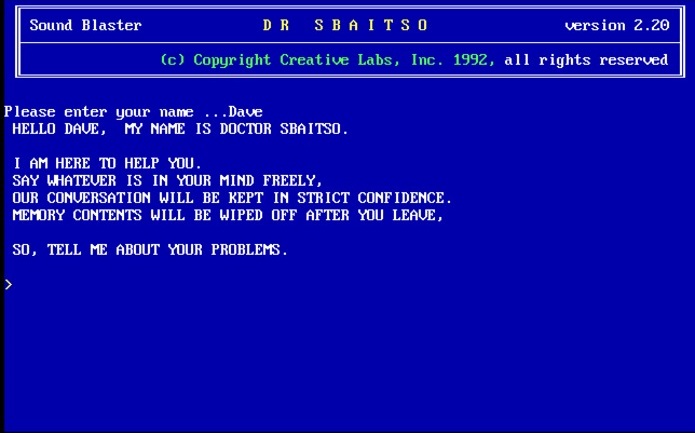
1992 - Dr. Sbaitso
Chatbot (Creative Labs)
A program that came with sound cards for MS-DOS. It showcased the digitized voices the cards were able to produce. Sbaitso was programmed to act like a very basic psychologist.
The quality of the voice was far from lifelike, and Sbaitso’s responses mostly were “WHY DO YOU FEEL THAT WAY?”

1995 - A.L.I.C.E. (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity)
Chatbot (Richard Wallace)
The program uses an XML Schema called AIML (Artificial Intelligence Markup Language) for specifying the heuristic conversation rules.[4]
Alice has won several Loebner awards and has been the inspiration behind the film “Her”, in which a man falls in love with a chatbot.
1995 - Albert One
Chatbot (Robby Garner)
Albert was designed to mimic the way humans make conversations. It won two awards for being most human at the Loebner awards in the end-90s.
A part of the program was available online in 1995, where it gathered information about what people would actually say to a chatbot.


1996 - Clippit
Virtual assistant (Microsoft)
Clippy shared tips and instructions to the user, based on the user’s actions in the Office programs.
The thought behind Clippy was that humans react to computers like they do to other humans. So Microsoft included a human-like face in their software. It was wildly unpopular, and has been made fun of by Microsoft later on.
The 2000s
2000 - Ultra HAL
Chatbot / Virtual assistant (Zabaware, Inc)
An information manager that users can interact with via typing or a speech recognition engine. It’s still in development, and has been so since its first mention in 2000.
A forerunner for the virtual assistants that’s a staple of most smartphones today.

2001 - Smarterchild
Chatbot / Virtual assistant (ActiveBuddy Inc)
The first bot made with instant message and social platforms in mind. Smarterchild started out as a word-based adventure game, but soon included instant access to news, weather, stock services, as well as tools like calculators and translators.
The forerunner of Siri, Alexa and other virtual assistants.
2006 - Watson
Question answering computer (IBM)
A program made to understand questions that humans ask and to provide answers that humans can understand and justify.
Watson appeared on Jeopardy, but the prelude wasn’t without challenges. A conflict ensued about whether the show would take advantage of the bots cognitive inferiority. On top of that, Jeopardy ruled that Watson should use the buzzer physically. All was solved with unused questions from earlier shows, and a robotic buzzer-hand for Watson. Watson won first place.

The 2010s
2005 - Mitsuku
Chatbot (Steve Worswick)
Winner of several Loebner awards, Mitsuku was built on ALICE’s framework. It’s still a work in progress, with additions from user-generated conversations.
When asked about something, Mitsuku looks up the properties for said thing to find a good reply (E.g. if asked if you can eat a house, it looks up what a house is made of. Since it’s bricks, it will answer that you can’t eat a house)
2010 - Siri
Virtual assistant (Apple / SRI International )
25 years after “The Knowledge Navigator”, Siri was launched, and set the tone for all the other virtual device assistants that followed this decade.
Originally, Siri was not owned by Apple, and was scheduled for release for both Android and blackberry. After only 2 months, Apple bought Siri.


2012 - Google Now
Virtual assistant (Google)
The assistant was developed from the “Google voice search” functionality. It stood out because it could remind users of events without being asked, based on the information Google had on the user. This in turn sparked some discussions about just how much data Google has on its users.
It was originally codenamed “Majel” after the actress who was the voice of computer systems in Star Trek.
2014 - Alexa
Virtual assistant (Amazon)
First made available in the Amazon Echo speaker, Alexa can do a lot of the standard virtual assistant stuff. It can also order things from Amazon, and control smart devices, turning it into a home automation system.
It got its name because the X can be recognized with higher precision. The voice of Alexa was also inspired by the Star Trek franchise.


2014 - Cortana
Virtual assistant, voice-based (Microsoft)
Another virtual assistant, this one is for Windows operating systems. It’s named after the A.I. character “Cortana” from the Halo video games, and voiced by the voice actress from the games.
2016 - Chatbots for Messenger
Chatbots (Facebook / Other companies)
In 2016 Facebook Messenger announced that they would open up for companies to have chatbots on Messenger.
The first generation of chatbots ranged from being well-received but very basic, to awful and unnecessary. The first generation was compared to the first generation of crappy apps made when smartphones caught on big time.

2016 - Tay
Chatbot (Microsoft)
Tay, presented as a curious teenager persona, was made available on Twitter. It made its tweets by analysing text, images and emojis from its interactions with other Twitter users.
It took teh interwebz less than 16 hours to get the bot to post profanities, conspiracy theories, and crude racial remarks. The bot managed to tweet more than 96,000 times before being shut down.
2017 - Bixby
Virtual assistant, voice-based (Samsung)
Samsung also wanted to be a part of the virtual assistant hype, so they made Bixby. It currently resides in my personal phone, and is mean at beatboxing.

The Loebner prize awards
The annual Loebner prize awards has since 1991 held contests for artificial intelligences. The bot considered the most human-like by the judges, win a money prize.


